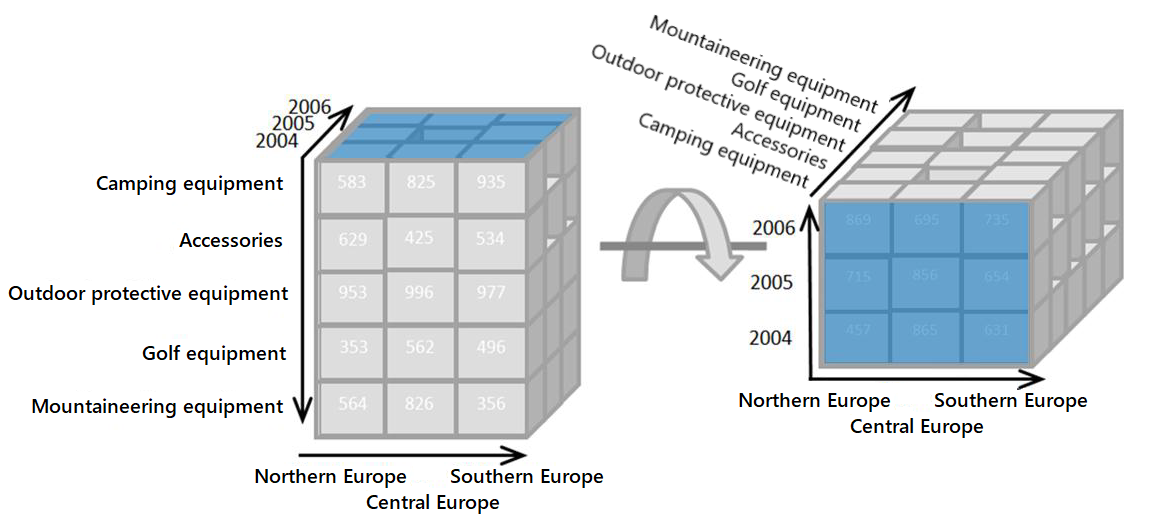
What is neuroplasticity?

Neuroplasticity, also known as neural plasticity, is the brain’s ability to reorganize and adapt its structure and function in response to experience, learning, or injury. This dynamic process allows the brain to form new neural connections, strengthen existing ones, and sometimes even reorganize itself to compensate for lost or damaged functions.
Key Aspects of Neuroplasticity:
1. Types of Neuroplasticity:
- Structural Plasticity: Changes in the physical structure of the brain, such as the formation of new neurons or changes in the size and number of synapses (the connections between neurons). This can occur in response to learning new skills, environmental changes, or recovery from injury.
- Functional Plasticity: The brain’s ability to shift functions from damaged areas to healthy ones. For example, if one part of the brain is injured, another part may take over its function to compensate for the loss.
2. Mechanisms of Neuroplasticity:
- Synaptic Plasticity: Changes in the strength or efficiency of synaptic connections between neurons. This includes Long-Term Potentiation (LTP), where repeated stimulation strengthens synapses, and Long-Term Depression (LTD), where synapses become weaker.
- Neurogenesis: The process of creating new neurons, primarily observed in the hippocampus, a region associated with learning and memory. While neurogenesis is most prominent during development, it can continue in certain brain areas throughout life.
3. Factors Influencing Neuroplasticity:
- Experience and Learning: Engaging in new activities, learning new skills, and cognitive challenges can promote neuroplasticity. For example, learning a new language or musical instrument can lead to structural changes in the brain.
- Environmental Stimuli: Environments rich in sensory experiences, social interactions, and cognitive challenges can enhance neuroplasticity.
- Recovery from Injury: After brain injury or stroke, neuroplasticity can help in recovery by reassigning functions to healthy brain regions.
- Lifestyle Factors: Physical exercise, a balanced diet, and adequate sleep contribute to neuroplasticity by supporting overall brain health.
4. Clinical Applications of Neuroplasticity:
- Rehabilitation: Neuroplasticity is harnessed in therapies for stroke and brain injury recovery, where targeted exercises and therapies help rewire the brain to regain lost functions.
- Mental Health: Understanding neuroplasticity has led to therapeutic approaches for mental health conditions. Techniques like Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) work by altering neural pathways associated with negative thought patterns.
- Learning and Education: Neuroplasticity research supports the development of educational strategies and tools that enhance learning by leveraging the brain’s ability to adapt and reorganize.
5. Limitations and Challenges:
- Age and Plasticity: While neuroplasticity occurs throughout life, it tends to be more pronounced in younger individuals. However, adults can still experience significant plasticity, especially with targeted interventions.
- Rehabilitation Limits: The extent of recovery through neuroplasticity can vary depending on the severity of the injury and the brain’s ability to adapt.
Examples of Neuroplasticity in Action:
- Skill Acquisition: Learning to play a musical instrument or mastering a new skill leads to changes in brain regions involved in motor control and sensory processing.
- Recovery from Stroke: Following a stroke, patients may regain lost abilities through therapy that encourages the brain to adapt and reroute functions to unaffected areas.
How to use neuroplasticity?
Harnessing neuroplasticity involves engaging in activities and practices that stimulate the brain’s ability to adapt and reorganize. Here are several strategies and methods to effectively utilize neuroplasticity for various purposes:
1. Learning and Skill Development
- Practice Regularly: Repeatedly practicing a new skill or activity, such as learning a language or playing a musical instrument, strengthens neural connections related to that skill. Consistent practice leads to structural changes in the brain, enhancing proficiency.
- Challenge Yourself: Engage in activities that push you out of your comfort zone. Complex tasks, puzzles, and learning new concepts can stimulate brain plasticity and improve cognitive abilities.
2. Mental Exercises and Cognitive Training
- Brain Games: Use brain training apps or games that target memory, problem-solving, and attention. These activities can help improve cognitive functions and promote neural growth.
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Practices such as mindfulness meditation have been shown to enhance brain connectivity and increase gray matter density in areas associated with attention, emotion regulation, and self-awareness.
3. Physical Exercise
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in physical activity increases blood flow to the brain, supports neurogenesis, and enhances cognitive function. Activities like aerobic exercise, strength training, and yoga contribute to overall brain health.
- Movement and Coordination: Exercises that require coordination and balance, such as dancing or martial arts, stimulate brain areas involved in motor control and spatial awareness.
4. Healthy Lifestyle Choices
- Balanced Diet: Consuming a diet rich in nutrients, antioxidants, and healthy fats supports brain health. Foods like berries, nuts, fish, and leafy greens are beneficial for cognitive function.
- Adequate Sleep: Ensuring you get enough quality sleep is crucial for memory consolidation and brain repair. Sleep supports neuroplasticity by reinforcing new learning and clearing out waste products from the brain.
5. Recovery and Rehabilitation
- Rehabilitation Therapies: For individuals recovering from brain injuries or strokes, targeted rehabilitation therapies can help rewire the brain and restore lost functions. These may include physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy.
- Adaptive Techniques: Using assistive devices and techniques tailored to individual needs can aid in regaining lost abilities and improving quality of life.
6. Emotional and Psychological Health
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT and similar therapeutic approaches work by helping individuals reframe negative thought patterns and modify maladaptive behaviors. This process can lead to changes in neural pathways related to mood and cognition.
- Stress Management: Managing stress through relaxation techniques, social support, and self-care can prevent negative effects on the brain and promote healthy neural functioning.
Also Read : What is Biological Neural Networks (BNNs)?
7. Social Engagement
- Social Interaction: Engaging in social activities and maintaining strong relationships stimulate cognitive functions and emotional well-being. Social interactions challenge the brain and promote neural connectivity.
- Community Involvement: Participating in community activities or volunteering can provide new experiences and cognitive stimulation, further supporting neuroplasticity.
8. Learning New Languages or Skills
- Language Learning: Learning a new language improves cognitive flexibility and strengthens neural connections in areas related to language processing and memory.
- Skill Acquisition: Acquiring new skills, whether related to hobbies or professional development, encourages brain adaptation and growth.
9. Creative Activities
- Art and Music: Engaging in creative activities like painting, drawing, or playing music stimulates different parts of the brain and enhances neural plasticity. Creative pursuits encourage problem-solving and innovative thinking.
10. Mind-Body Practices
- Yoga and Tai Chi: These practices combine physical movement, meditation, and mindfulness, which can improve brain function, enhance emotional regulation, and support neuroplasticity.
Conclusion
Utilizing neuroplasticity involves actively engaging in activities that stimulate and challenge the brain, promoting adaptive changes and growth. By incorporating a combination of cognitive, physical, and emotional practices into daily life, individuals can enhance their brain function, support recovery, and improve overall well-being.
FAQ
1. What is neuroplasticity?
Neuroplasticity is the brain’s ability to reorganize and adapt its structure and function in response to experience, learning, or injury. It involves forming new neural connections, strengthening existing ones, and sometimes reassigning functions to different areas of the brain.
2. How can I use neuroplasticity to improve learning and skill development?
– Practice Regularly: Repeated practice of new skills, such as learning a language or playing an instrument, strengthens neural connections related to those skills.
– Challenge Yourself: Engage in complex tasks and new experiences to stimulate brain adaptation and growth.
3. What are some mental exercises that promote neuroplasticity?
– Brain Games: Use apps or puzzles that challenge memory, problem-solving, and attention.
– Mindfulness and Meditation: Practices like mindfulness meditation can enhance brain connectivity and increase gray matter density.