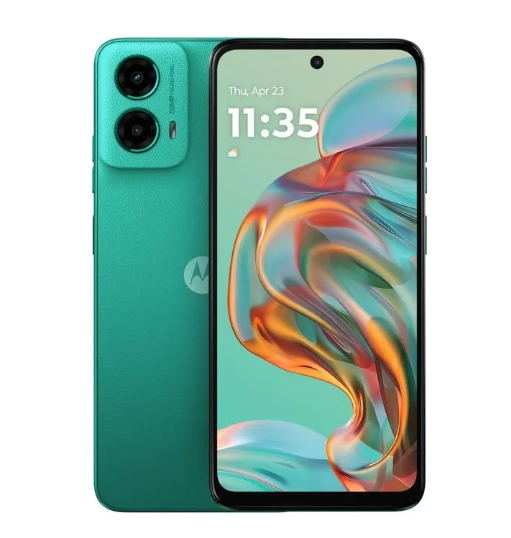
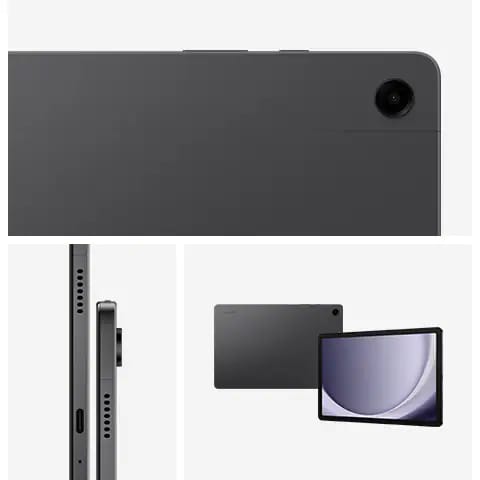
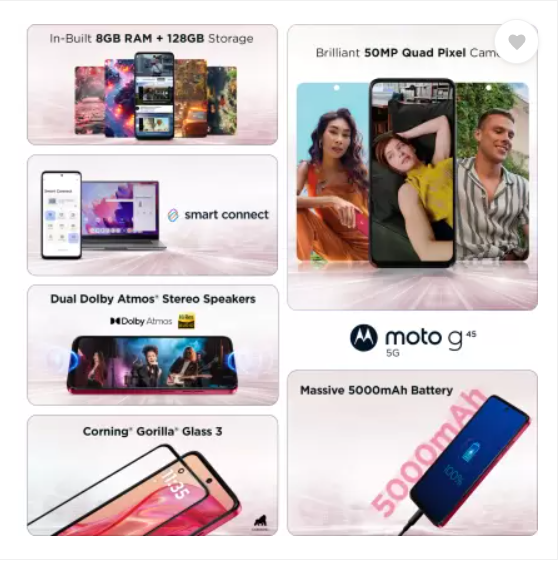
Motorola g45 5G स्मार्टफोन अत्याधुनिक तकनीक और बेहतरीन फीचर्स के साथ आता है। यह Snapdragon 6s Gen 3 प्रोसेसर और LPDDR4X मेमोरी के साथ आता है, जो तेज़ परफॉर्मेंस और Seamless 5G Experience देता है। Motorola g45 5G का 50MP Quad Pixel कैमरा शानदार फोटोग्राफी सुनिश्चित करता है, वहीं 16MP फ्रंट कैमरा आपकी सेल्फी को और खास बनाता है।
Dolby Atmos और Hi-Res ऑडियो के साथ Dual Stereo Speakers आपको क्रिस्टल-क्लियर साउंड अनुभव दैता है। 6.5 inch का HD+ 120Hz IPS LCD डिस्प्ले smooth और Vibrant visuals के लिए परफेक्ट है। IP52 water-repellent design और Gorilla Glass 3 प्रोटेक्शन इसे मजबूत और टिकाऊ बनाते हैं। तो चलिए Motorola g45 के बारे में विस्तार से जानकारी प्राप्त करना शुरू करते हैं

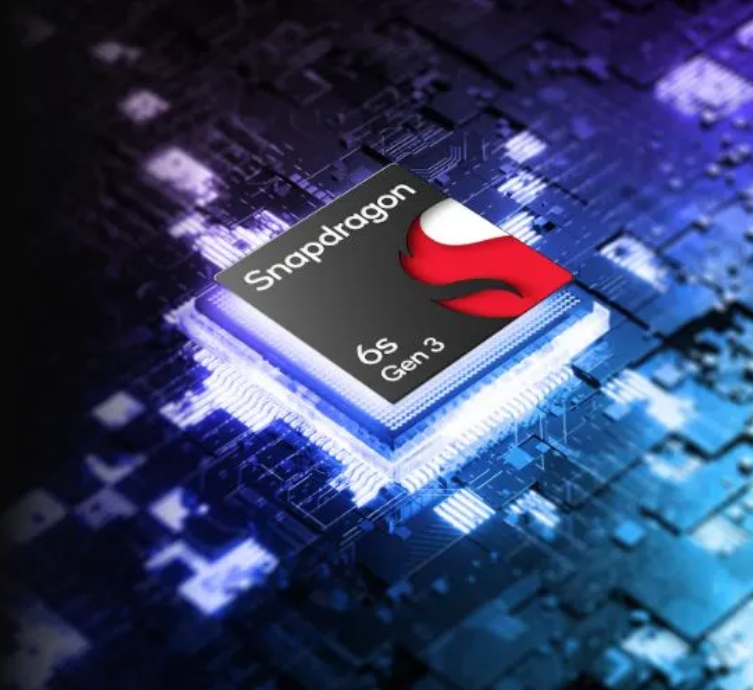
Processor – Snapdragon 6s Gen 3
Motorola g45 5G आपके लिए लाया है अगली पीढ़ी का Snapdragon 6s Gen 3 प्रोसेसर। यह Octa-core Processor और LPDDR4X memory से लैस है, जो इसे अपने सेगमेंट का सबसे तेज़ और दमदार स्मार्टफोन बनाता है। Blazing-fast 5G speeds का अनुभव करें, seamless gaming, smooth multitasking, और stunning low-light photos का आनंद लें। इसकी lightning-fast downloads और unbeatable efficiency इसे एक अच्छा फ़ोन बनाती है।
Motorola g45 5G: HD+ 120Hz IPS LCD Display
Motorola g45 5G के डिस्प्ले फीचर्स इसे और भी आकर्षक बनाते हैं:
- डिस्प्ले साइज: 6.5 inch (16.51 cm)
- रिज़ॉल्यूशन: 1600 x 720 pixels (HD+)
- डिस्प्ले टाइप: HD+ 120Hz IPS LCD
- रिफ्रेश रेट: 120Hz, जो smooth scrolling और बेहतर गेमिंग अनुभव प्रदान करता है।
- आस्पेक्ट रेशियो: 20:9
- स्क्रीन-टू-बॉडी रेशियो: 85%, जिससे edge-to-edge display का अनुभव मिलता है।
- GPU: Qualcomm Adreno 619, बेहतर ग्राफिक्स परफॉर्मेंस के लिए।
Motorola g45 5G डिस्प्ले क्वालिटी आपको वीडियो स्ट्रीमिंग, गेमिंग, और ब्राउज़िंग के दौरान एक immersive visual experience देती है।
Also check: ICC: Announcement on Hosting Arrangements for India and Pakistan Matches in ICC Events
Motorola g45 5G: Stereo Speakers with Dolby Atmos & Hi-Res Sound
Motorola g45 5G में आपको मिलेगा Dolby Atmos और dual stereo speakers का सपोर्ट, जो आपके ऑडियो अनुभव को redefine करता है। Hi-Res audio technology की मदद से आपको crystal-clear sound, rich bass, vibrant vocals और enhanced clarity का अनुभव होता है। चाहे आप मूवी देख रहे हों, म्यूजिक सुन रहे हों या गेम खेल रहे हों, इसकी multidimensional sound आपको हर मोमेंट में डुबो देगी।
IP52 Water-repellent Design + Gorilla Glass 3 Protection
Motorola g45 5G का IP52 Water-repellent design आपके स्मार्टफोन को spills और splashes से सुरक्षित रखता है। बारिश हो या जिम में पसीना, यह फोन हर Situation के लिए तैयार है। साथ ही, Gorilla Glass 3 protection आपके फोन को scratches और external damages से बचाता है, जिससे इसका durability level और भी बढ़ जाता है।
Motorola g45 5G: 50 MP Quad Pixel Camera with Image Auto Enhance
Motorola g45 5G की 50 MP Quad Pixel Camera के साथ capture करें stunning photos, चाहे लाइटिंग कैसी भी हो। इसका advanced camera sensor और Image Auto Enhance feature आपकी हर फोटो को Instagram-ready बनाता है। Macro Vision से छोटे से छोटे details को capture करें और 16MP front camera से अपनी selfies को एक नया आयाम दें।
Motorola g45 5G: HD+ 120Hz IPS LCD Display
Motorola g45 5G में 6.5 इंच का HD+ 120Hz IPS LCD Display दिया गया है, जो 1600×720 pixels resolution और 20:9 aspect ratio के साथ आता है। 120Hz refresh rate के साथ smoother scrolling और बेहतर गेमिंग अनुभव मिलता है। 85% screen-to-body ratio आपको edge-to-edge display का बेहतरीन अनुभव देता है।
Motorola g45 5G: Operating System और Processor
Motorola g45 5G फोन Android 14 के साथ आता है, जो आपको लेटेस्ट फीचर्स और seamless यूजर एक्सपीरियंस देता है। Snapdragon 6s Gen 3 Octa-core processor इसकी स्पीड और परफॉर्मेंस को unmatched बनाता है।
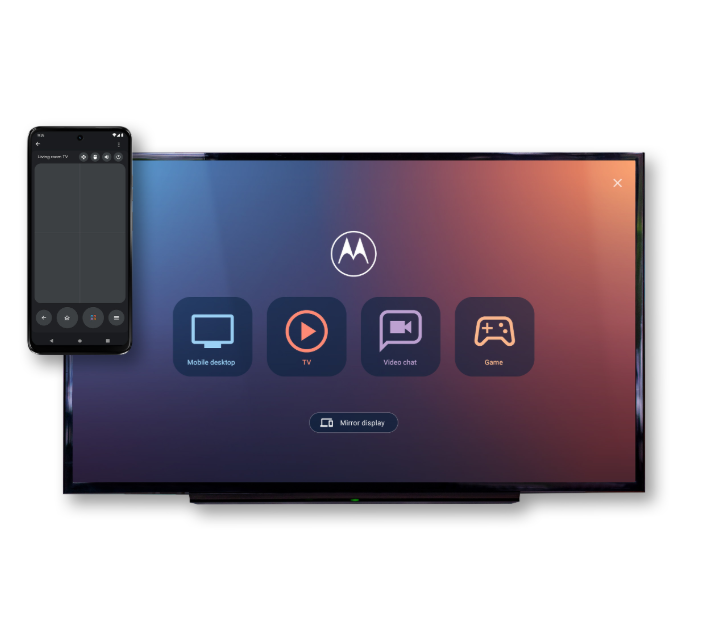

Motorola g45 5G: Unleash the Power of Connectivity
8GB वेरिएंट में एक खास फीचर है, जो आपको अपने स्मार्टफोन को वायरलेस तरीके से TV या monitor से कनेक्ट करने की सुविधा देता है। आप अपनी apps का इस्तेमाल कर सकते हैं, वीडियो कॉल कर सकते हैं, गेम खेल सकते हैं और अपने मोबाइल की क्षमताओं को amplify कर सकते हैं।
Motorola g45 5G, आधुनिक टेक्नोलॉजी और पावरफुल फीचर्स का परफेक्ट कॉम्बिनेशन है। चाहे आप गेमिंग के शौकीन हों, फोटोग्राफी के दीवाने, या एक multitasking expert, यह फोन आपकी हर जरूरत को पूरा करता है।